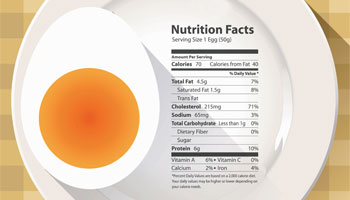
No matter how you break them, eggs are a healthy choice.
Eggs are an excellent source of high quality protein plus they provide many vitamins and minerals, including vitamin B12, riboflavin, vitamin D, folate, choline and iron. Eggs are one of nature's most nutrient-dense foods.
Scroll down to find more
Eggs - Full of What Your Body Needs

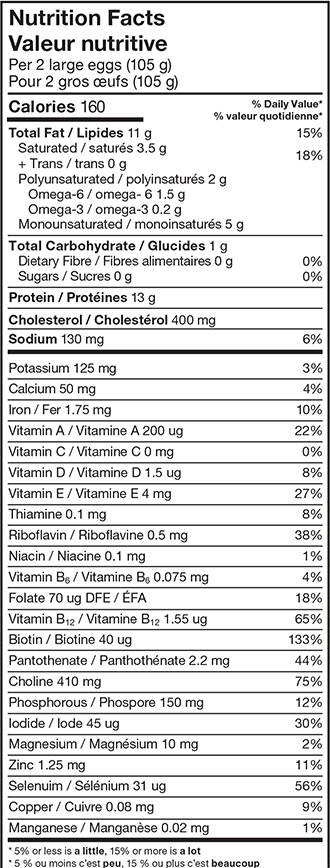
- Iron
- Carries oxygen to the cells; helps prevent anemia - the iron in eggs is easily absorbed by the body.
- Vitamin A
- Helps maintain healthy skin and eye tissue; assists in night vision
- Vitamin D
- Strengthens bones and teeth; may help protect against certain cancers and autoimmune diseases
- Vitamin E
- An antioxidant that plays a role in maintaining good health and preventing disease
- Vitamin B12
- Helps protect against heart disease
- Folate
- Helps produce and maintain new cells; helps prevent a type of anemia; helps protect against serious birth defects if taken prior to pregnancy and during the first 3 months of pregnancy.
- Protein
- Essential for building and repairing muscles, organs, skin, hair and other body tissues; needed to produce hormones, enzymes and antibodies; the protein in eggs is easily absorbed by the body.
- Selenium
- Works with vitamin E to act as an antioxidant to help prevent the breakdown of body tissues.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin
- Maintains good vision; may help reduce the risk of age-related eye diseases such as cataracts and macular degeneration.
- Choline
- Plays a strong role in brain development and function
The Importance of Protein
A number of bodily functions are dependent on the presence of protein in the diet, or more specifically, amino acids. Our bodies digest dietary proteins and break them down to amino acids, which are then shipped off to different parts of the body.
Eggs are considered a 'complete protein' as they contain all nine essential amino acids along with a wide array of other vitamins and minerals. The natural protein from an egg is best-absorbed and utilized by the body, and therefore egg protein is considered to be the gold standard of protein quality. All other protein sources are measured with respect to the egg.
Protein is an important part of every cell in the body, it is needed to:
- build and repair body tissue
- help fight infections
- help keep body fluids in balance
- serve as enzymes and hormones
- help the body maintain a healthy metabolism
- supply energy (calories) so the body can function
Did You Know...
Egg whites contain only half of the egg’s protein, so it is important to eat the whole egg to fully enjoy its energy boosting potential.
Egg Protein Provides Lasting Energy
Protein-rich eggs provide lasting energy because protein helps control the rate at which food energy (calories) is absorbed. This means including protein at every meal occasion will help sustain your energy level and keep you active longer.
Egg Protein can Help You Lose Weight
In a recent study, an egg-based breakfast was compared to a bagel-based breakfast containing the same number of calories. Researchers found those who ate two eggs and toast for breakfast lost 65% more weight, had an 83% greater reduction in waist circumference and experienced higher energy levels than those who ate a bagel and yogurt for breakfast.
Biological Value of Egg Protein
Eggs have the highest biological value of any food protein, which means the amino acids found in eggs are converted into body tissue more efficiently than any other known dietary protein. Egg protein (along with milk and soy protein) possesses the highest possible Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS), the most commonly used measure of protein quality. One large egg contains about 6 grams of high-quality protein, which makes it an ideally-packaged amino acid component for refueling after exercise.